Clinical Therapy
Clinical therapy typically refers to psychological or mental health counseling provided by licensed therapists or counselors. For those with late-onset Tay-Sachs disease, clinical therapy offers emotional support, coping strategies, and mental health care to manage the emotional and psychological impact of the disease. This therapy is vital for addressing depression, anxiety, or other mental health challenges that may accompany chronic illness, providing a holistic approach to care. (Pegboard, Rummikub, Majong)
One example of a Clinical Therapy exercise is using a Peg Board to sharpen motor skills. This exercise is done by inserting pegs into a wooden board. This exercise assists with sharpening motor skills and coordination.
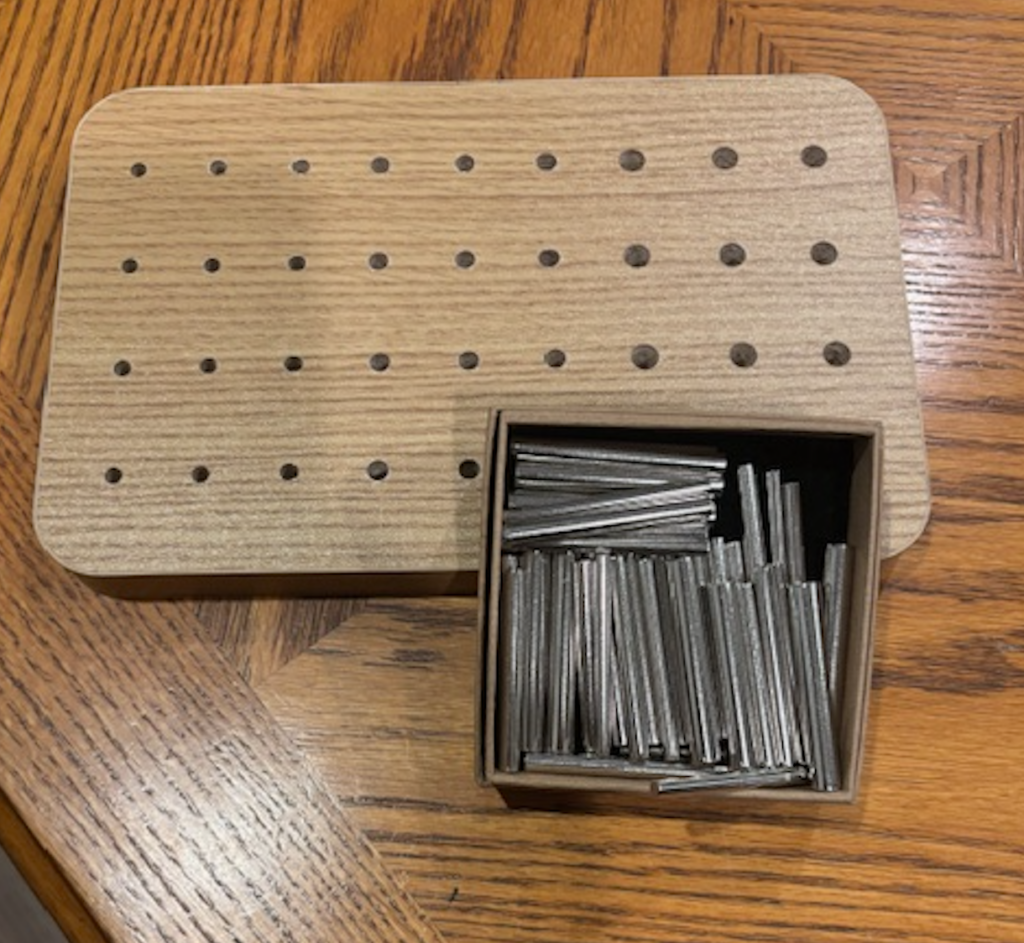
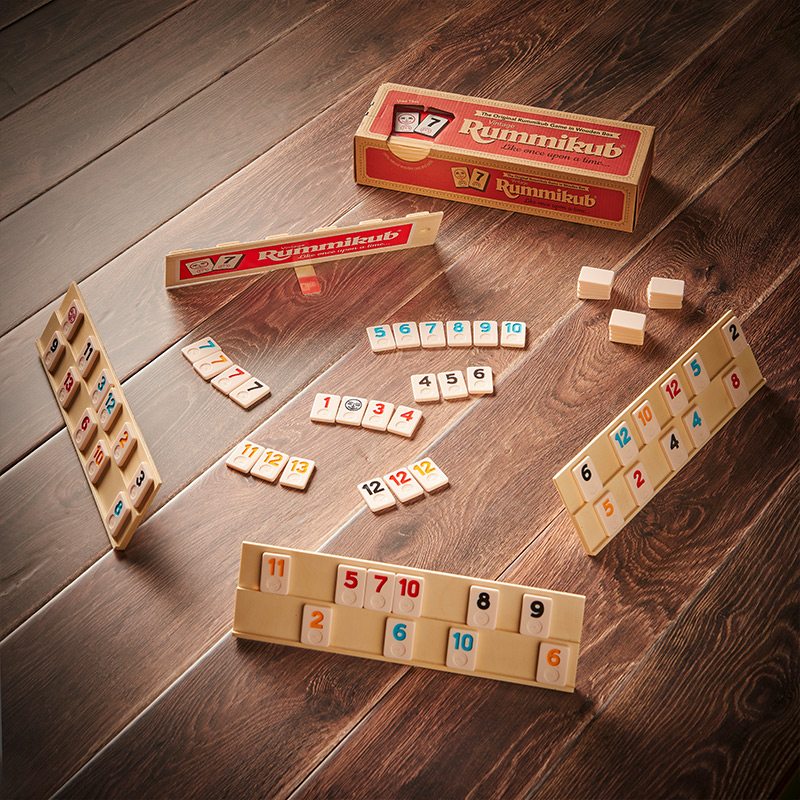



Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on helping individuals with physical, cognitive, or developmental challenges improve their ability to perform daily activities. For those with late-onset Tay-Sachs disease, occupational therapists work to enhance fine motor skills, strengthen muscles, and adapt the home or work environment to support greater independence. This therapy is essential for maintaining or improving the quality of life by addressing practical aspects of daily living, such as dressing, eating, and other self-care tasks.
One example of a Clinical Therapy exercise is using a Peg Board to sharpen motor skills. This exercise is done by inserting pegs into a wooden board. This exercise assists with sharpening motor skills and coordination.
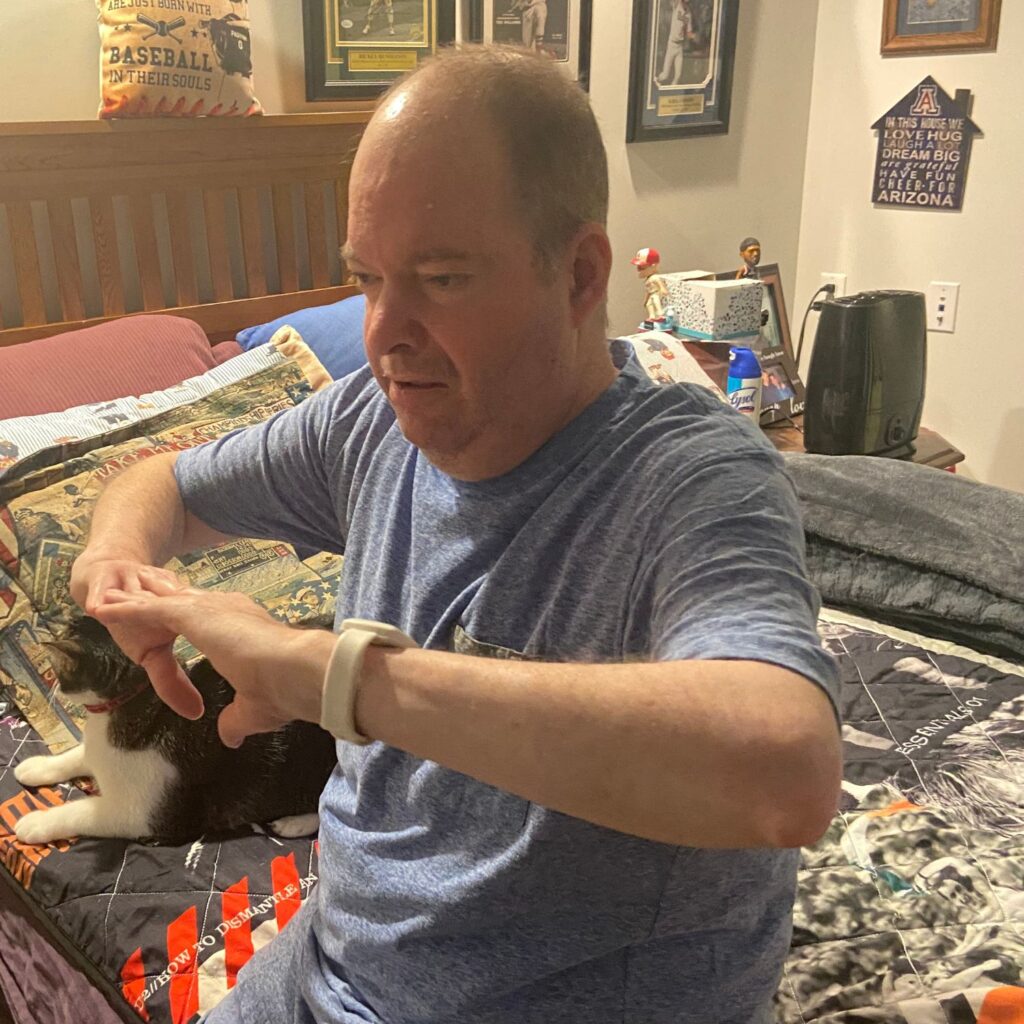
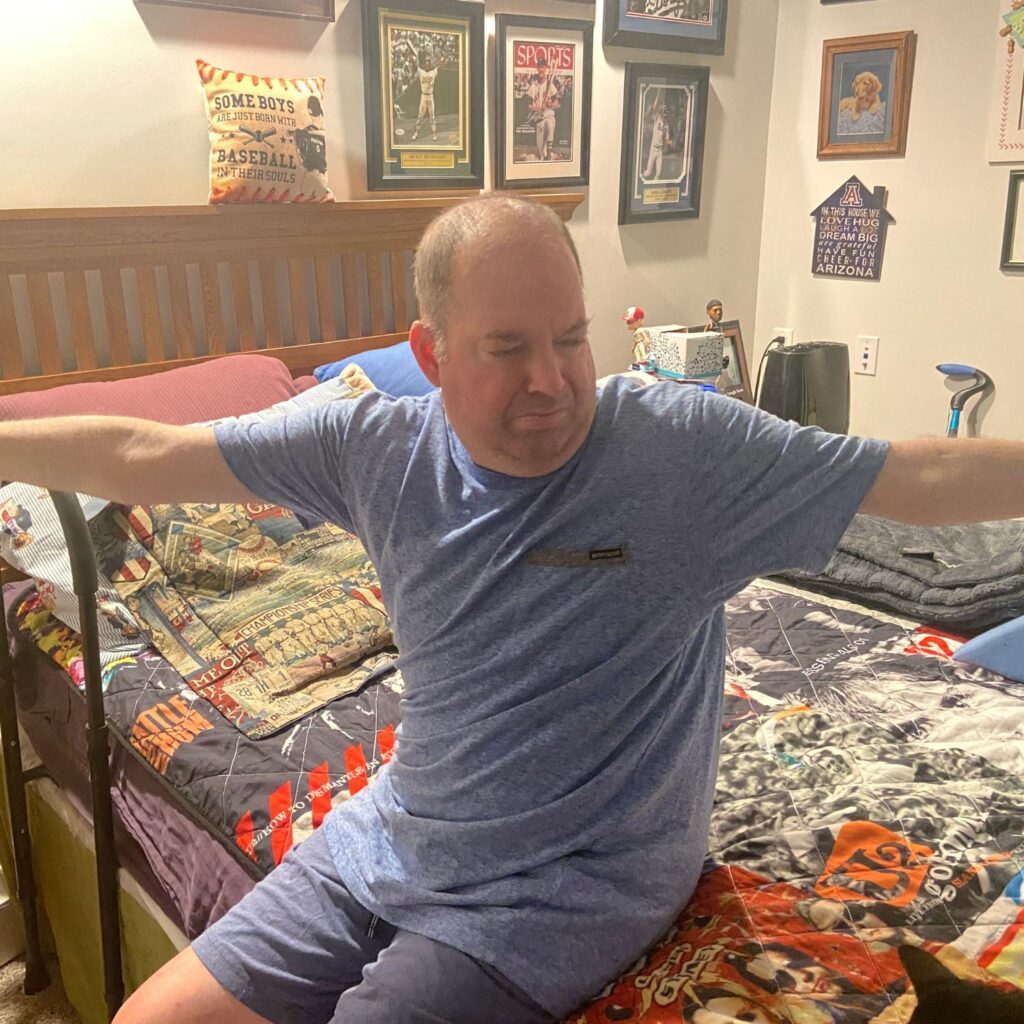
- Sit tall with your hands in front of you
- Keep your elbows high
- Both feet, or at least toes, touching the floor
- INHALE
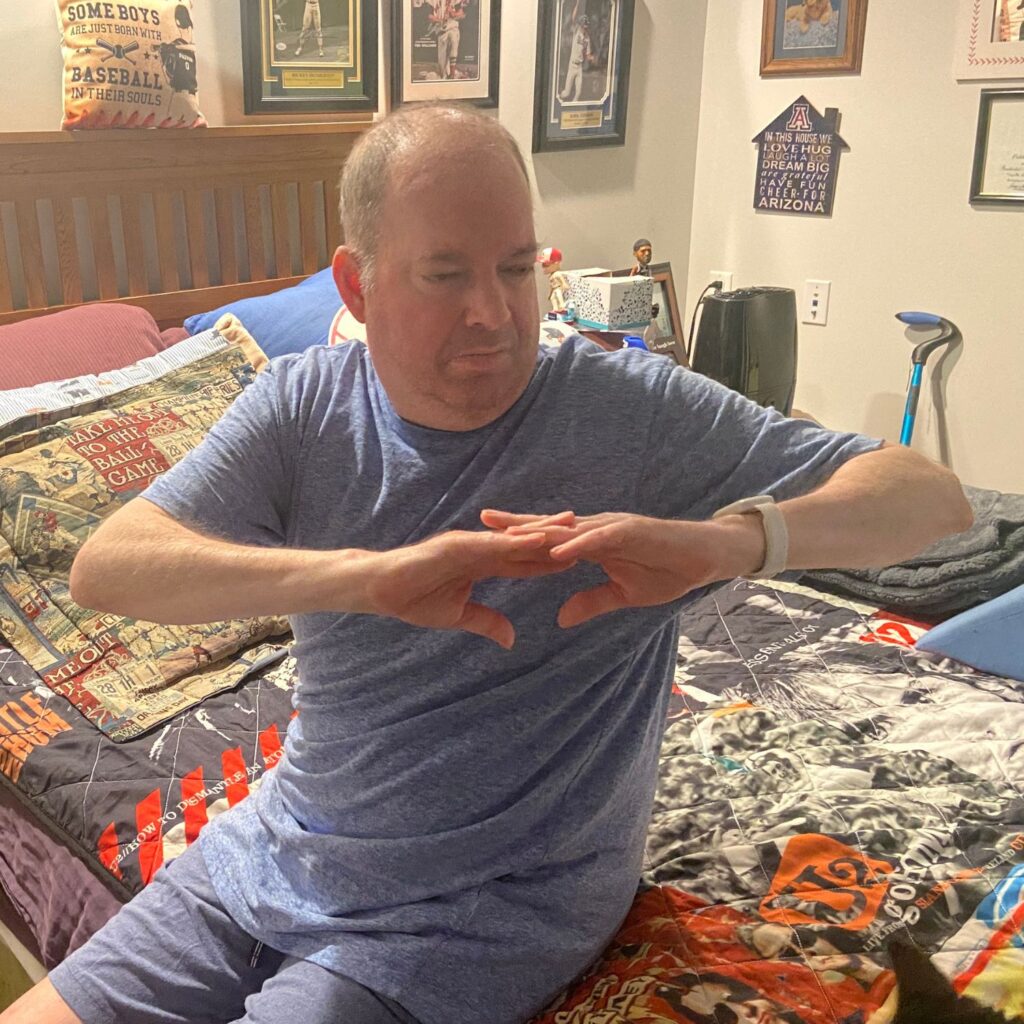

- EXHALE
- Turn “trunk” body toward TV

- INHALE
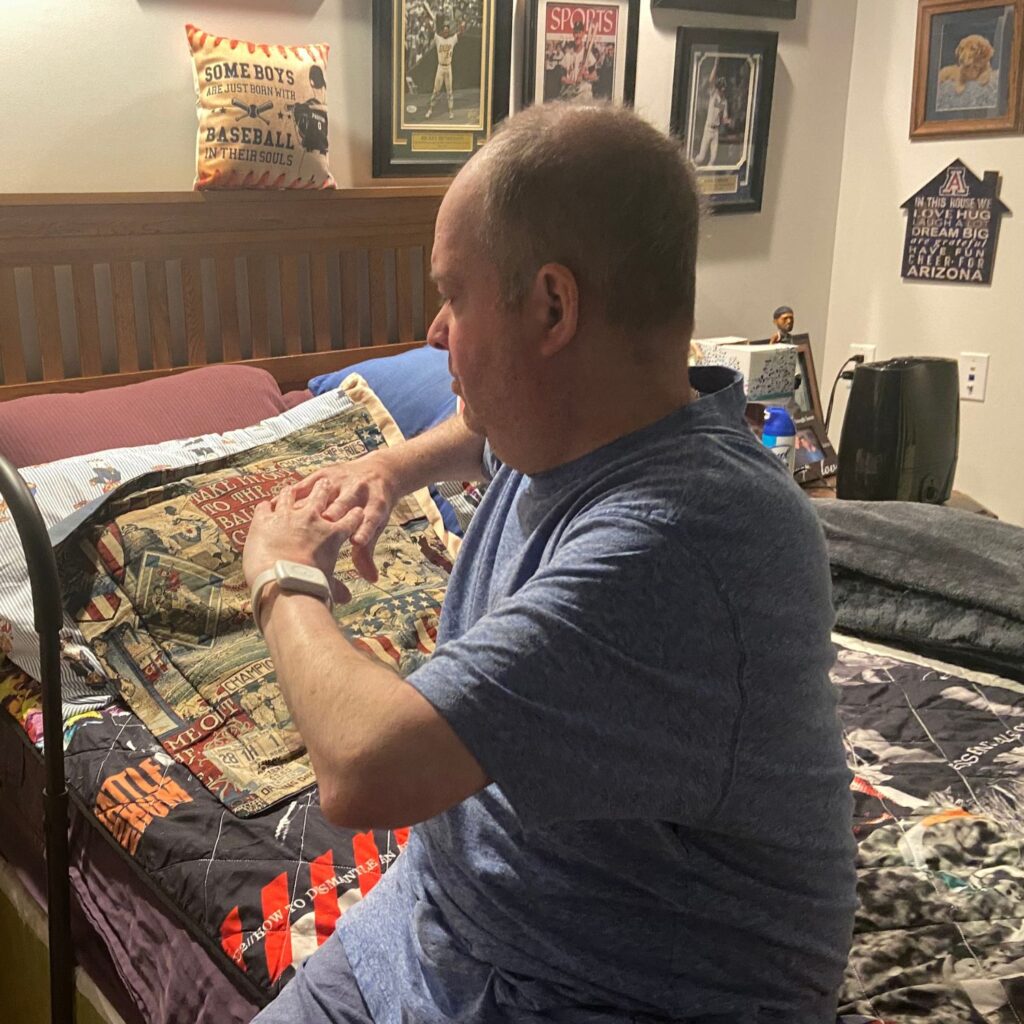
- EXHALE
- Open arms wide to sides!

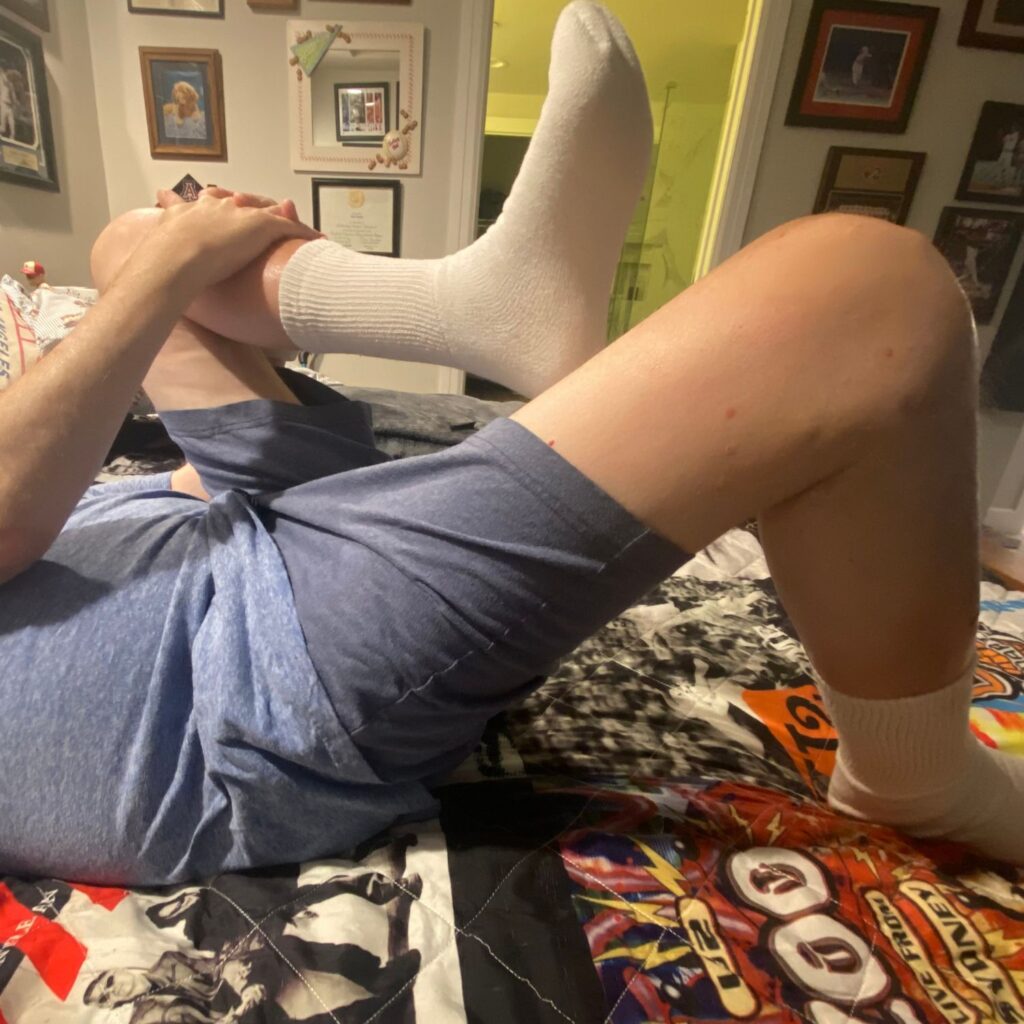
- Sit tall with your hands in front of you
- Keep your elbows high
- Both feet, or at least toes, touching the floor
- INHALE

- repeat?
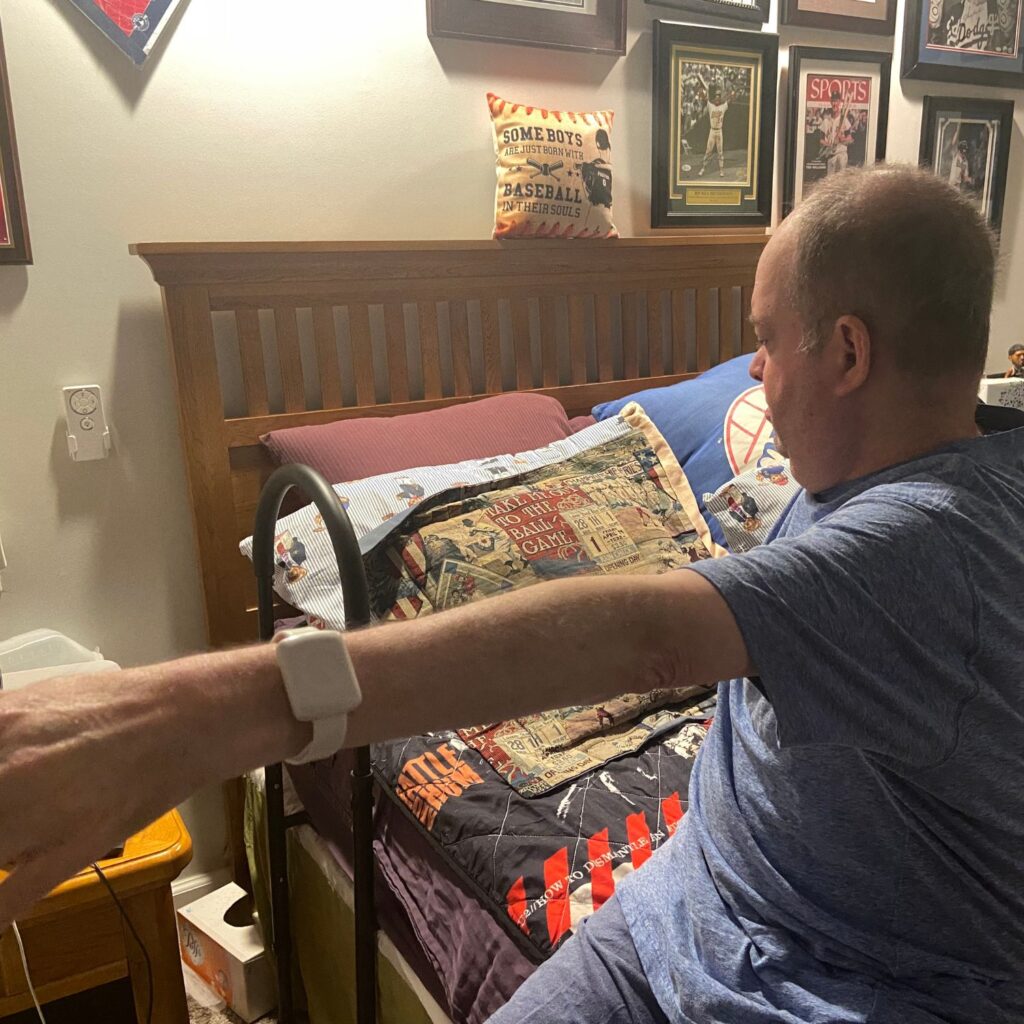

- repeat?

- repeat?
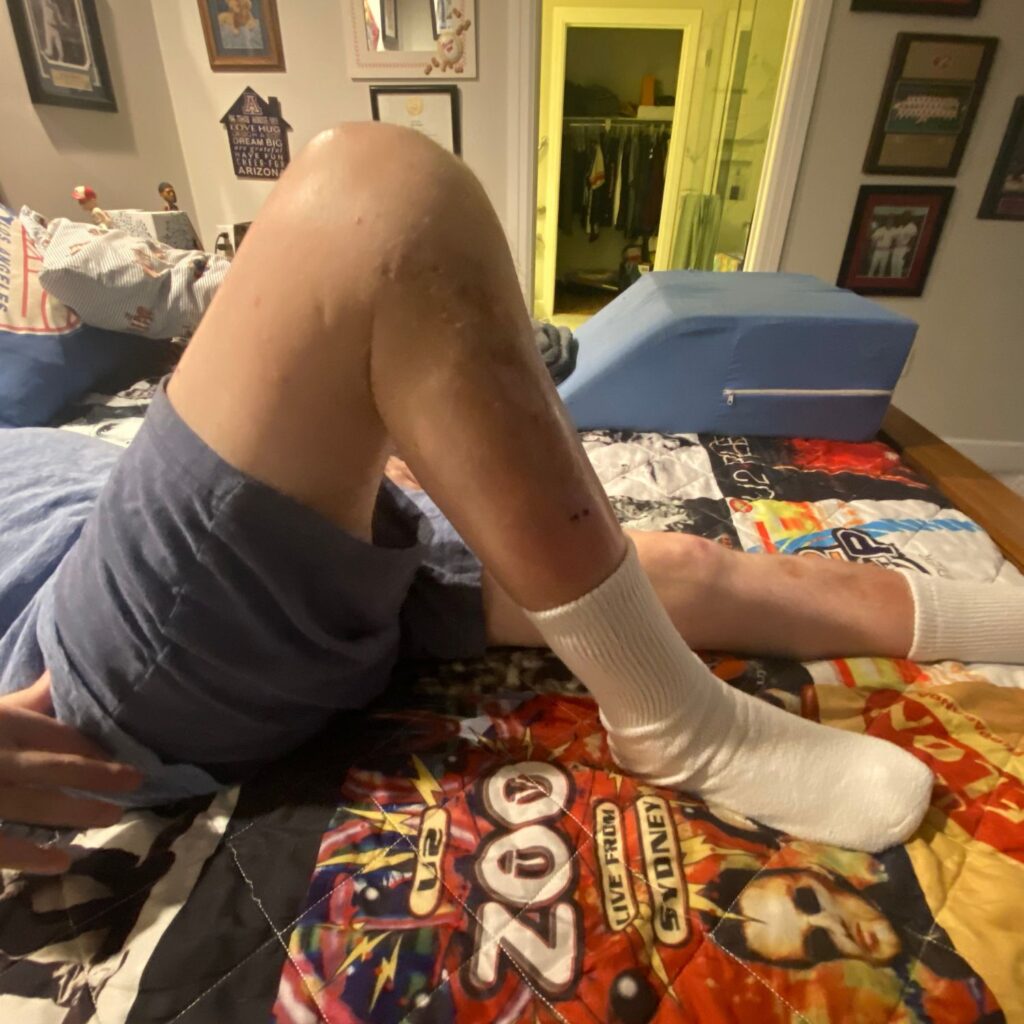
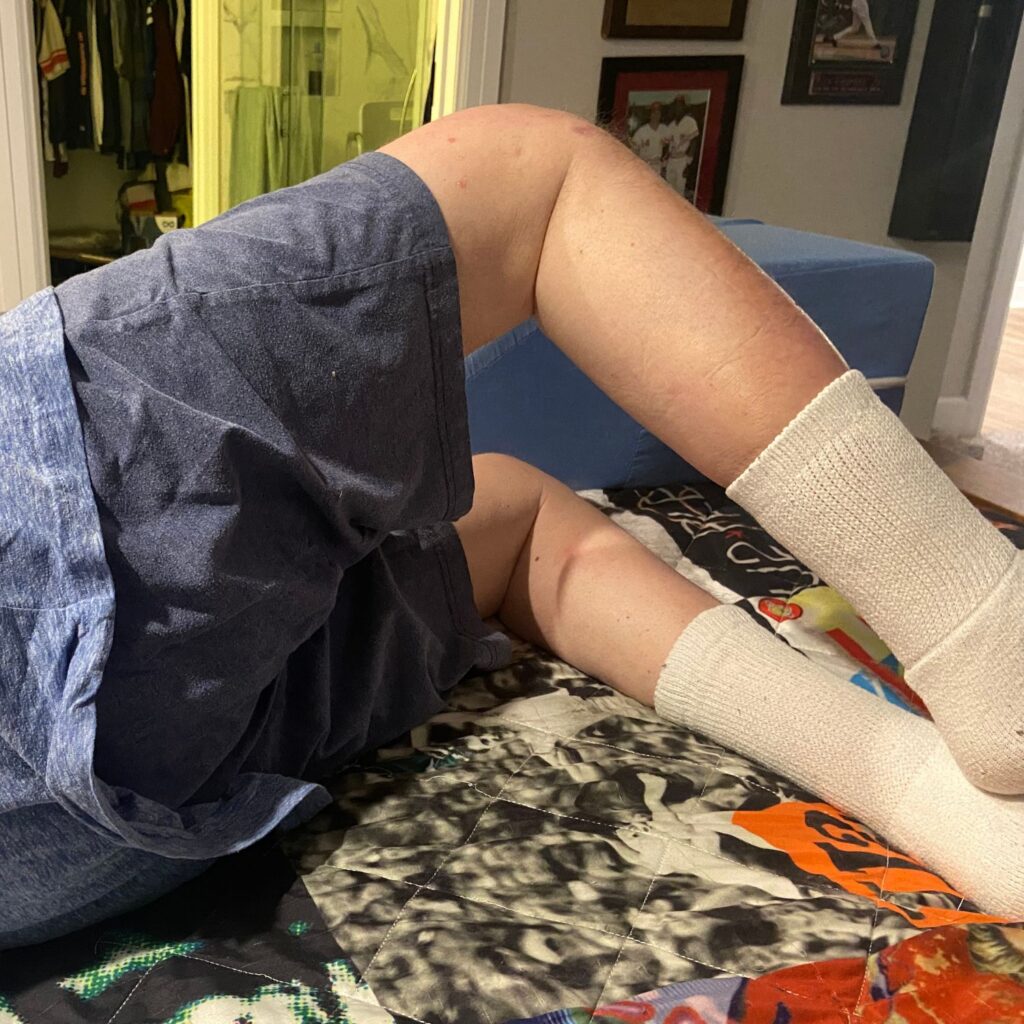
- Lay on your back
- Have one knee bent
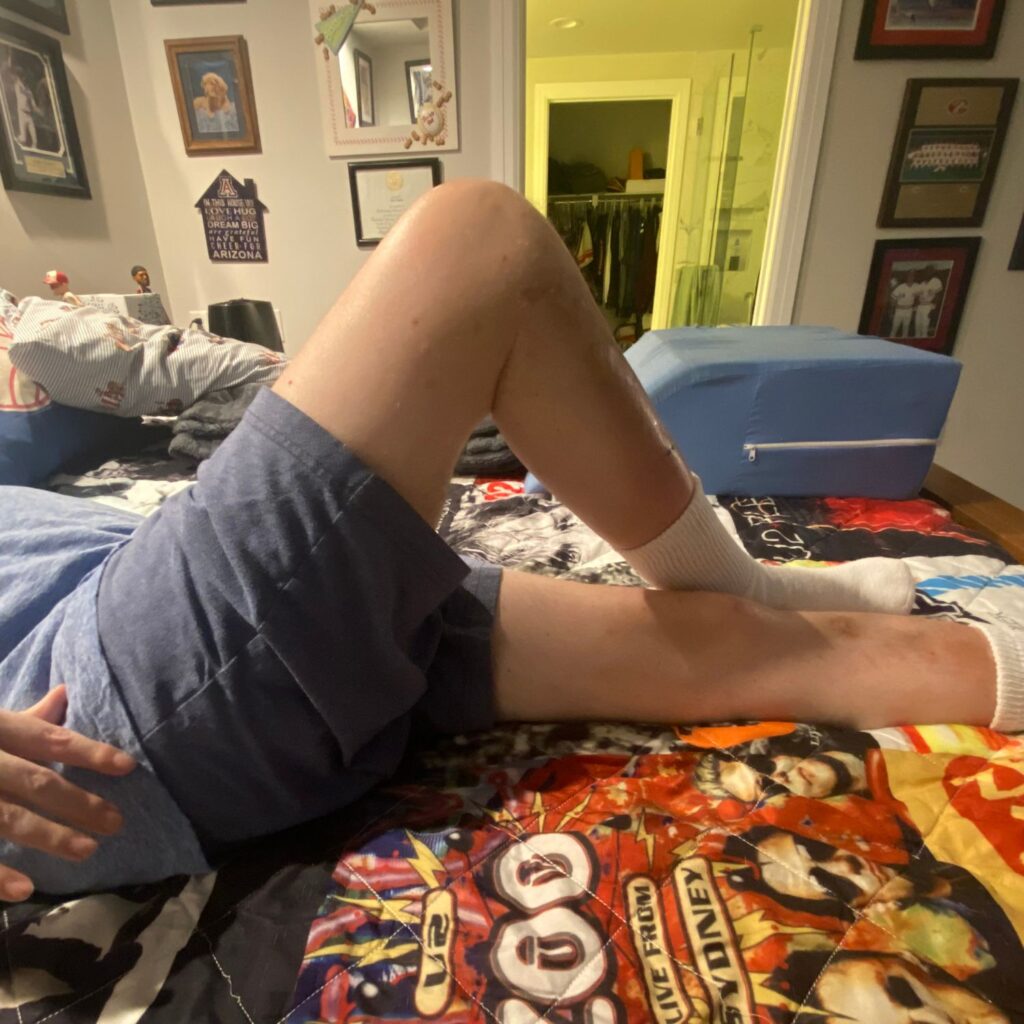

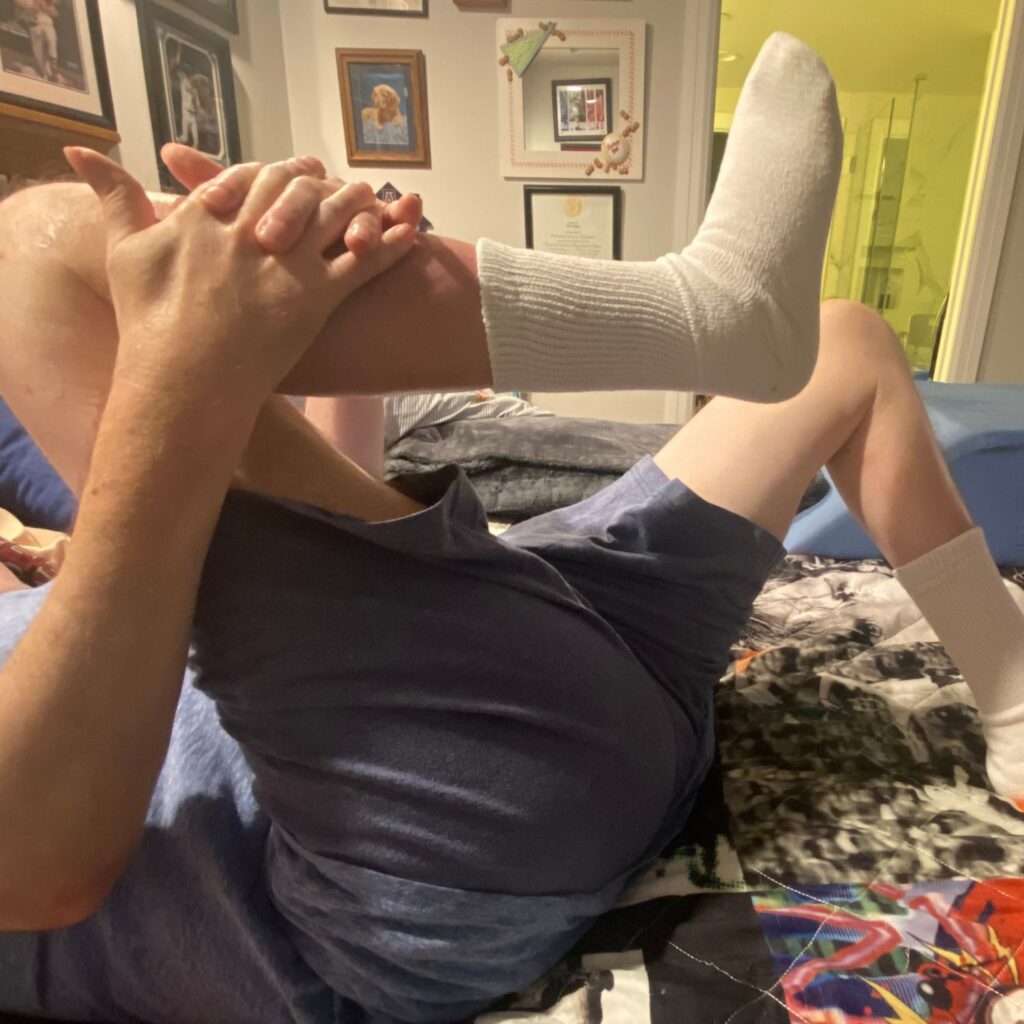
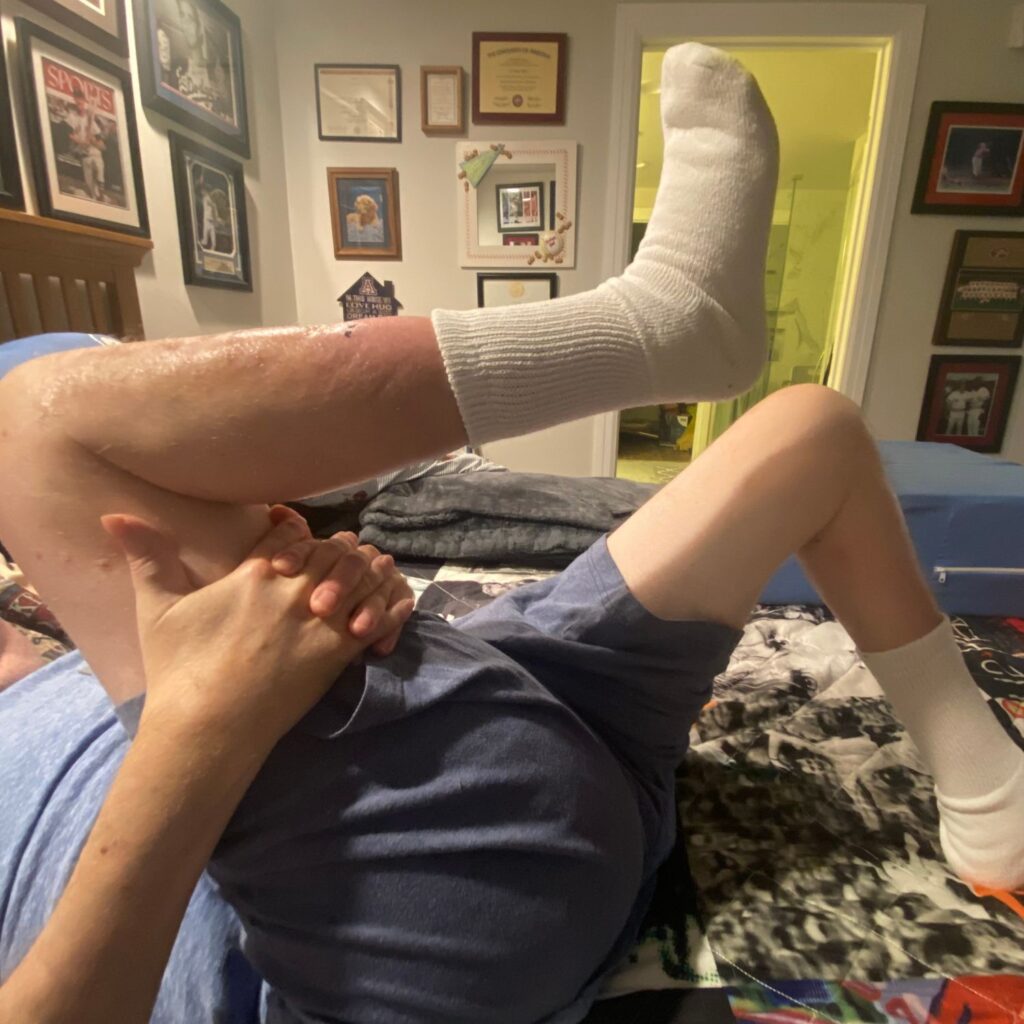
- Lay on your side
- Have knees bent
- INHALE
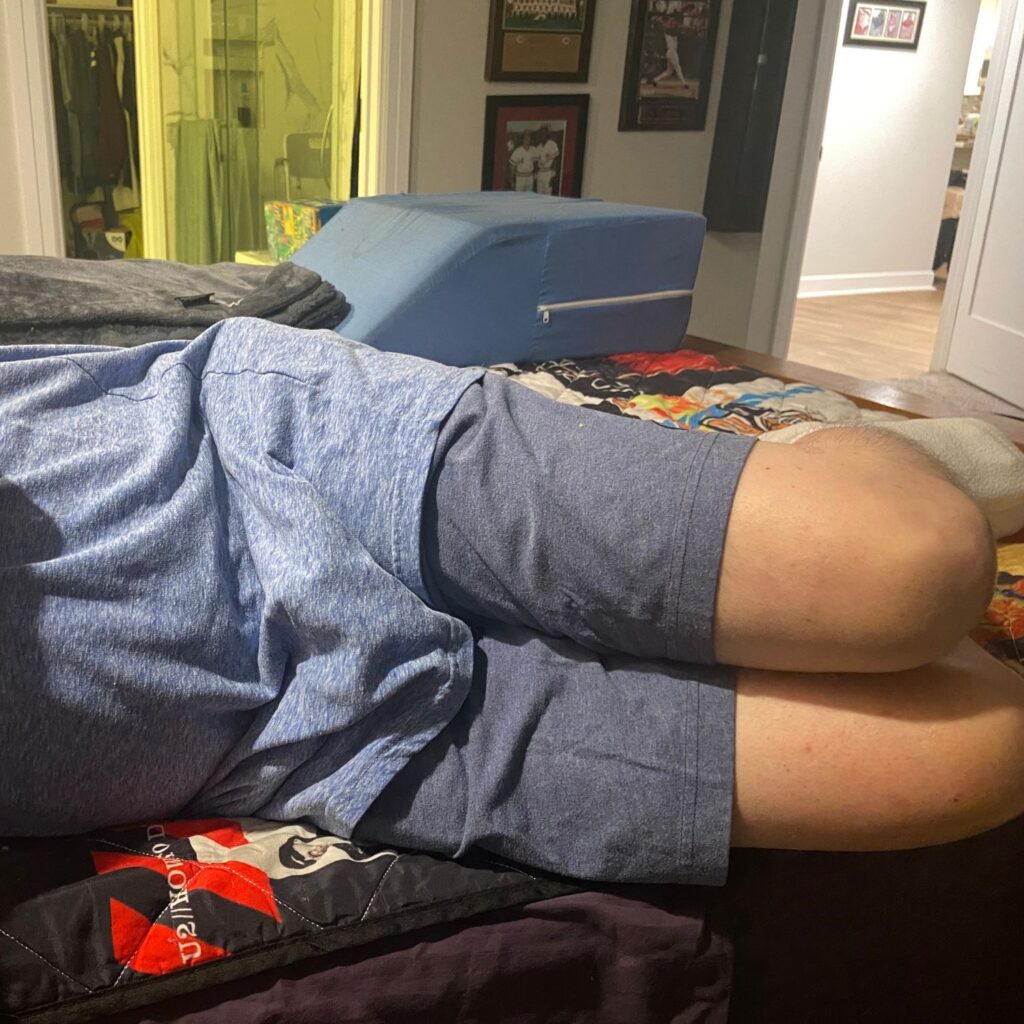
- Add
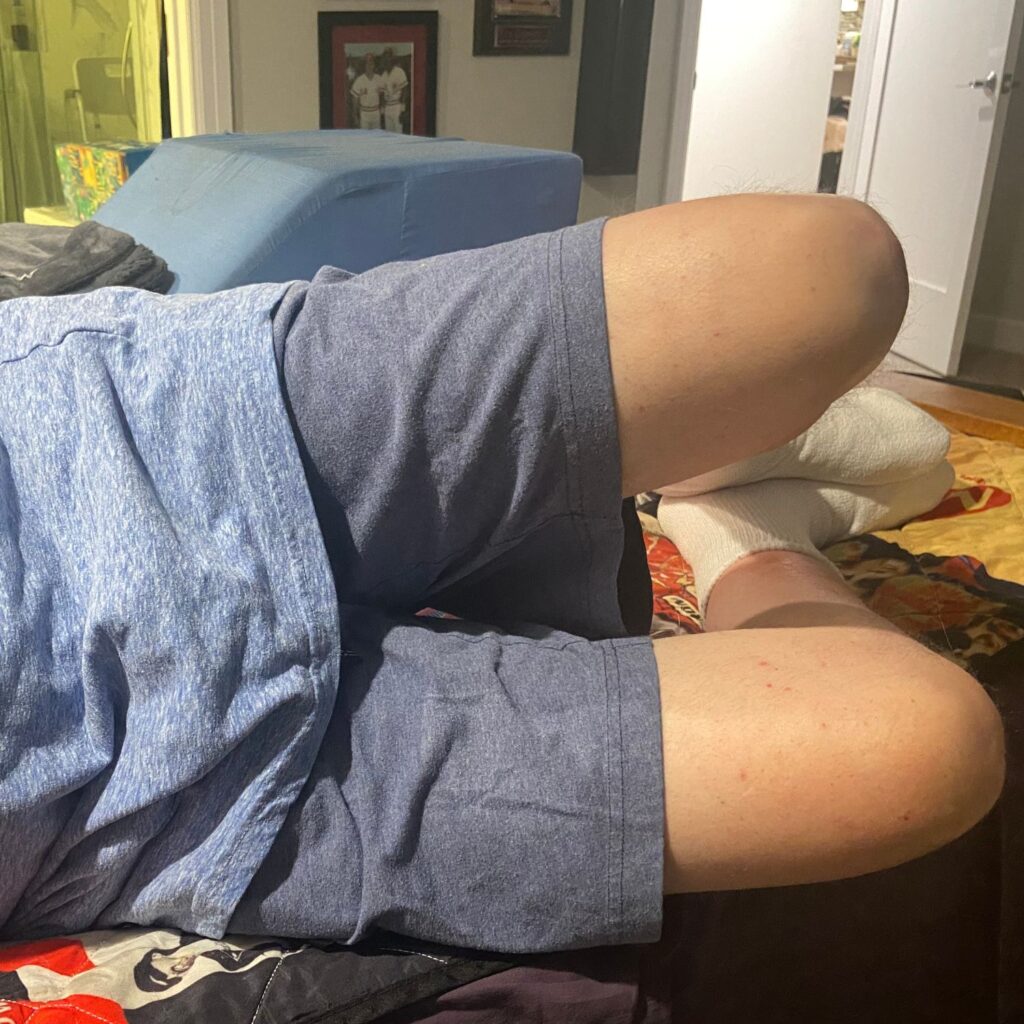

- Add
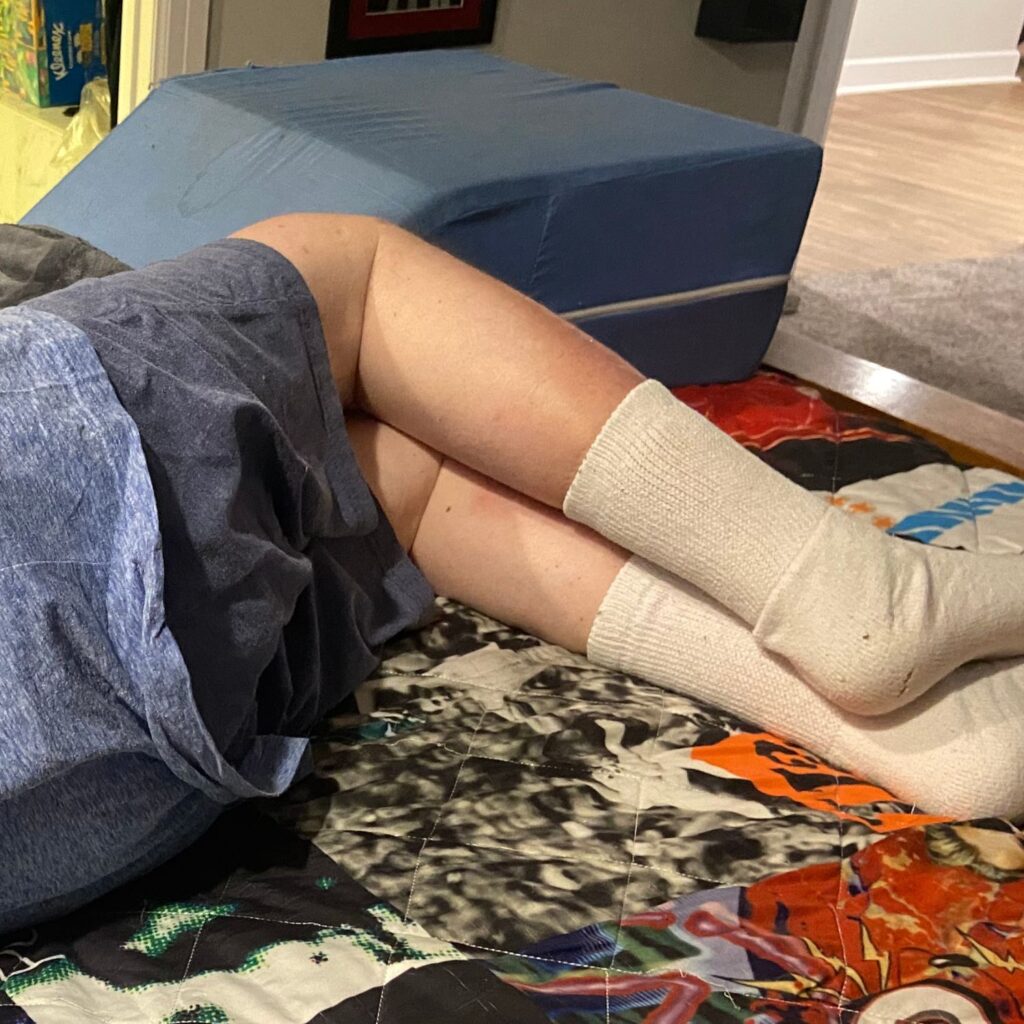
- Add
- Add

- Add
- Add
- Add
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy focuses on improving or maintaining physical function and mobility through targeted exercises and interventions. For individuals with late-onset Tay-Sachs disease, physical therapy is crucial in managing symptoms such as muscle weakness, coordination difficulties, and balance issues. A physical therapist designs a personalized exercise regimen that aims to strengthen muscles, enhance flexibility, and improve overall mobility. This therapy helps slow the progression of physical decline, reduces the risk of falls, and supports independence in daily activities. Additionally, physical therapy can assist in managing pain and fatigue, contributing to an improved quality of life.
One example of a Clinical Therapy exercise is using a Peg Board to sharpen motor skills. This exercise is done by inserting pegs into a wooden board. This exercise assists with sharpening motor skills and coordination.
Speech Therapy
Speech therapy addresses communication challenges, including difficulties with speaking, understanding language, swallowing, or cognitive-communication skills. For individuals with late-onset Tay-Sachs, speech therapists can assist in preserving speech abilities, improving articulation, and managing swallowing difficulties that may arise. This therapy is crucial in ensuring effective communication and safe eating practices, enhancing overall quality of life.
Each patient needs to be consistent to improve or maintain muscles in mouth, lips, or cheeks. It is a necessity to continually practice.
*add any disclaimer here…

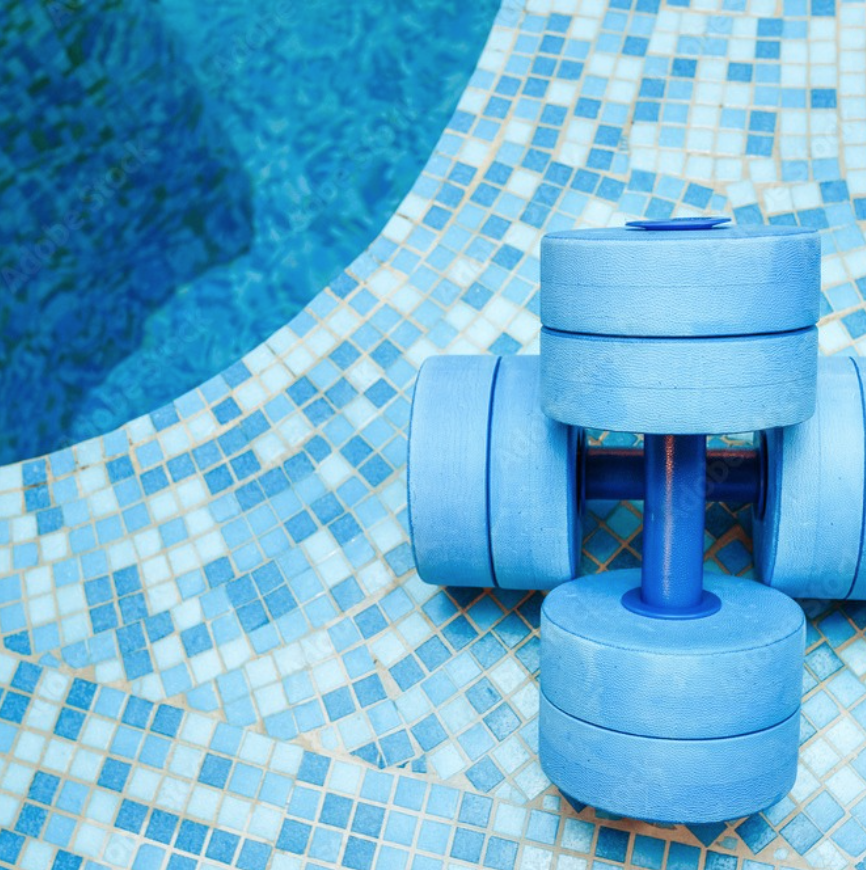
Aqua Therapy
Aqua therapy, also known as aquatic therapy, involves performing exercises and therapeutic activities in a warm water pool, leveraging the water’s buoyancy to reduce strain on the body. For individuals with late-onset Tay-Sachs disease, this form of therapy can be particularly beneficial as it allows for gentle, low-impact movement that can help maintain muscle strength, improve flexibility, and relieve joint pain. The water’s natural resistance aids in muscle strengthening, while the buoyancy provides a supportive environment that reduces the risk of injury and eases the strain on weakened muscles and joints. Aqua therapy also offers a relaxing and calming experience, which can positively impact both physical and mental well-being.
It is beneficial to find an inside pool that has a pool lift, ramp with bars and more people that are less affected with LOTS to use stairs with bars to go up and down . Once in the water you may need assistance as the assistant puts a noodle behind your back and floats. You may also walk having the water creating resistance as you walk. Other exercises include doggy paddle and sitting on noodles. Also, stretching bands in the water to improve strength.

The information provided on this website is intended for educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. While we aim to offer valuable suggestions for different types of therapy, it is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making any decisions regarding your treatment plan. Only a licensed medical professional can provide advice, diagnosis, or treatment tailored to your specific condition and needs. Your healthcare provider will be able to guide you in choosing the most appropriate therapy options for your individual situation.
